Italian Family History
Genealogy
in Italy

| History | Italian Family History |
 |
Italy and the world |
 |
|
In the upcoming centuries the efficient economic, political and military systems of Rome increased the power of the state which
became richer, developped in culture and civilization and enlarged its territories. |
 |
|
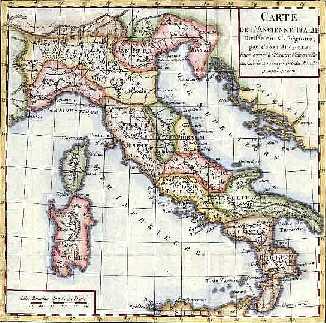
| South Italy was under the control of the Arabs and later Spain. Among these small political entities some rich "Maritime Republics" (Gaeta, Genova, Pisa, Venezia) conquered influence in
the East Mediterranean Sea. During the Middle ages Italy was ruled by small states, principalities and small kingdoms, which fought among themselves subject to foreign powers an to the Church. Rome became the see of the Pope and the Papal State became the centre of European spiritual power. The commercial and economic prosperity of the northern and central Italian cities gave origin to the Rinascimento. Tuscany, rulled by the De' Medici family, became the center of this cultural, artistic and scientific movement. At the beginning of the 16th century Italy suffered the effects of a political, economic and spiritual crisis. First the Reformation against the power and the corruption of the Church swapt away the geo-political power of the Catholic Church. To this the Church answered with the Counter-Reformation. Secondly the discovery of the America moved the center of world from the Mediterranean to the countries on the coast: France, Spain, Portugal, England. Most of the small and weak Italian states were rulled by foreign powers, some states (e.g. Milan and Naples) were annexed, others (e.g. Venice and Florence) were reduced to a lesser role. |
 |
|
In 1911 after a successful war with the Ottoman empire, Italy conquered part of Lybia and some islands in the Aegean Sea. After the First World War (1915-1918) and the annexation of new territories (Trento, Trieste, Istria, Dalmatia) strong social conflicts brought to power in 1922 Benito Mussolini. His fascists party installed a dictatorship that lasted twenty years. Fascism lead Italy into the Second Word War that ended in a bloody defeat and in a civil war. These tragic events were the foundations the Italian Republic in 1946. |